INTRODUCTION
Spinal extradural arachnoid cyst (SEAC) is a rare disease and uncommon cause of compressive myelopathy. SEAC is more commonly found among male patients and during the second decade of their life. SEACs can be found in any location, although mostly reported to be located at mid thoracic to the thoraco-lumbar junction, commonly in a posterior position1,3,4,6,10,12).
SEAC is an outpouching herniation of arachnoid membrane through a dural defect that may communicate to intradural subarachnoid space5). The etiology of this herniation is still unclear and can be either congenital or acquired6). These cysts can result in fluctuating symptoms associated with cord or root compression. It is assumed that they can be enlarged by subsequent pressure change in the cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) during exercise and Valsalva maneuvers as there is micro-communication between the cysts and subarachnoid space2,6).
Despite the rarity of SEACs, they are important in neurosurgical view because they are surgically curable disease. Diverse surgical techniques have been introduced and many reports reviewed favorable outcome of SEACs with surgical treatment. We experienced 2 cases of SEACs and performed cyst fenestration and primary repair of dural defects for all of them. The aim of this article is to illustrate our experience and review the literatures.
CASE REPORT
Case 1
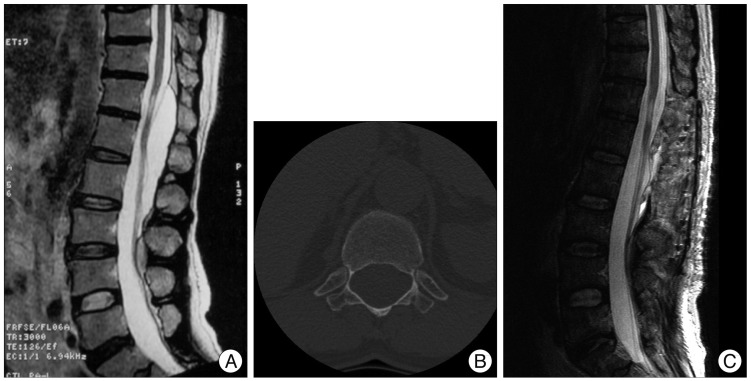
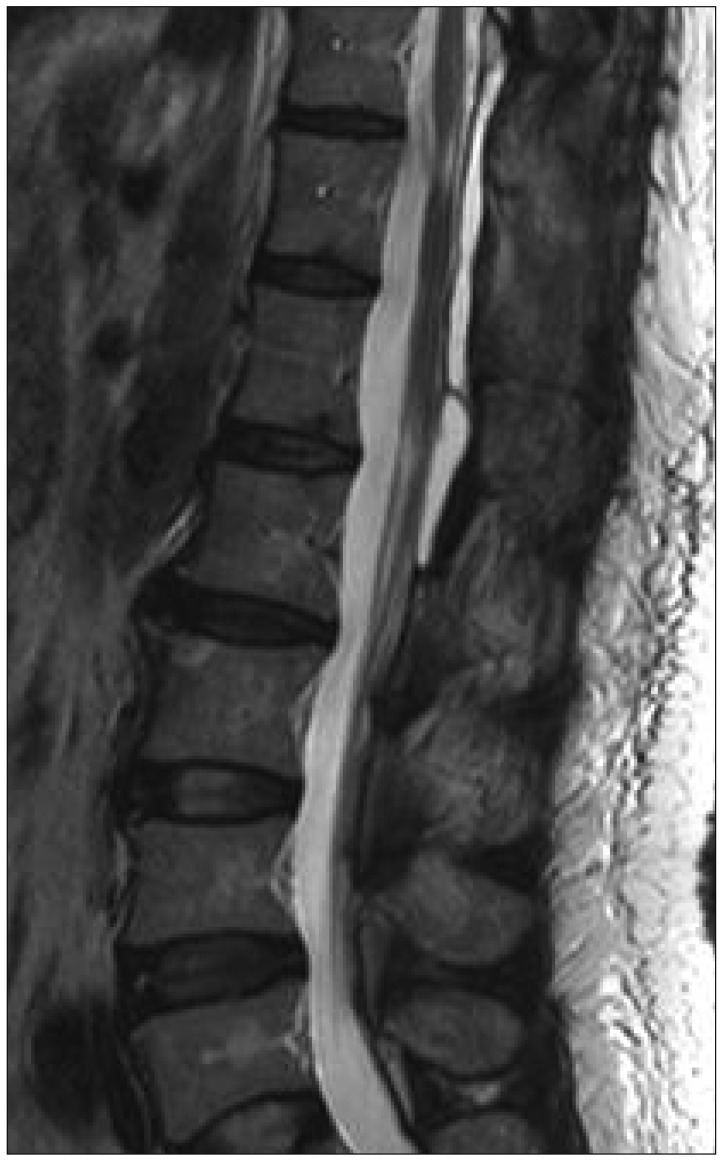
A 59-year-old man presented with both leg radiating pain and paresthesia for 4 years. Other physical findings were not remarkable. MRI showed a large, elongated posterior extradural cyst from T12 to L3 with surrounding bony erosion (Fig. 1A, B).
Thinned overlying laminas were found on operative field and the cyst was ruptured during laminectomy. There was a hole-like dural defect near to right L1 root sleeve and we performed primary closure of the defect. Some part of cyst wall was also removed.
The patient's symptoms were gradually subsided and follow up image taken 1 month after the operation showed complete disappearance of the cyst (Fig. 1C).
Case 2
A 51-year-old female patient visited our clinic with left buttock pain and paresthesia for 3 years. Her pain was aggravated on coughing and she also complained of gait disturbance with both sole numbness on walking.
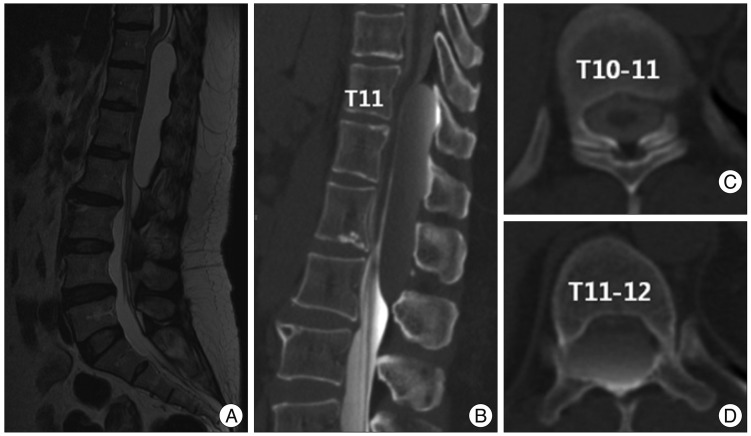
MRI showed a large extradural cyst located posterior to the cord from T11 to L2 (Fig. 2A). CT myelogram was performed to verify any communication between the subarachnoid space and the cyst (Fig. 2B, C, D). The contrast dye diffused within the subarachnoid space reaching to T11-12 level, and then leaked into the cyst. It scantly spreaded above the level and we assumed that there might be communication between the cyst and the subarchcnoid cyst at T11-12 level.
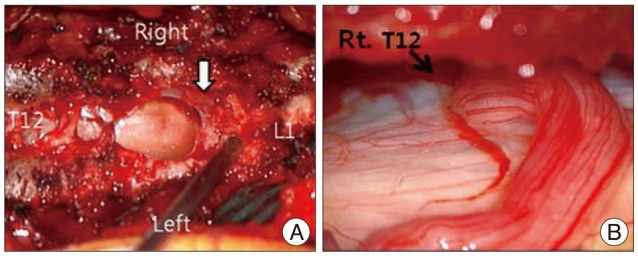
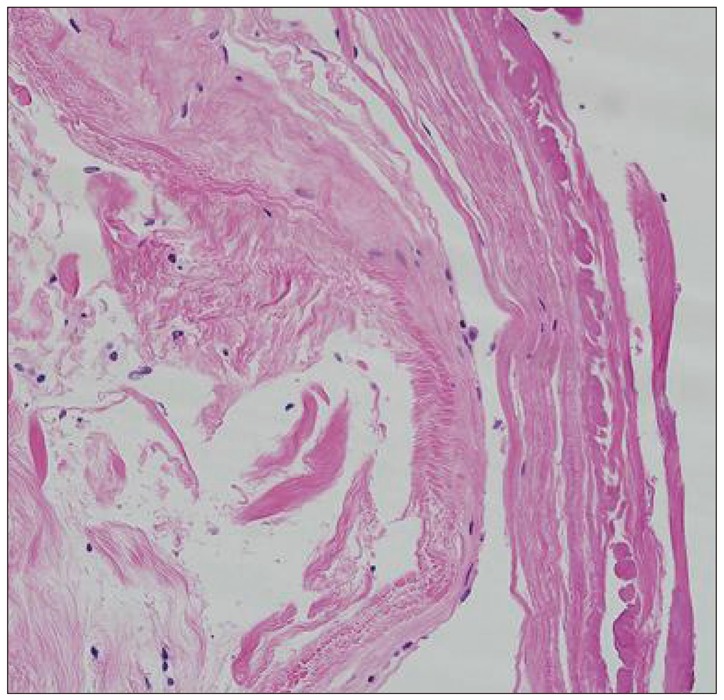
At first, total laminectomy of T10 and T11 was planned to find a dural defect. The laminae overlying the cyst were thinned. The cyst wall was ruptured during laminectomy and CSF-like fluid was gushed out. Under microscopic exploration, transparent cyst wall was found at the margin of bony exposure (Fig. 3A). There was a hole-like, 0.5 cm sized dural defect at the right posterolateral side of the dural sac at T11 level. A rootlet got caught in the dural defect and formed a loop around the hole (Fig. 3B). The root was repositioned into the intradural space and the dural defect was repaired with black silk 6-0. The cyst wall was severely adherent to the dural sac and there was moderate bleeding on dissecting the cyst. We only fenestrated the cyst. Some portion of the cyst wall was removed and sent to pathologic department. Pathologic findings were compatible to arachnoid cyst (Fig. 4).
Her symptoms relieved gradually and follow up MRI taken at 2months after the operation showed much decreased cyst and there was no evidence of cord compression due to residual cyst (Fig. 5).
DISCUSSION
SEAC is a rare disease entity accounting for 1% of all spinal tumors10). These cysts may originate in protrusion of arachnoid membrane through a dural defect and may be enlarged by CSF accumulation. When enlarged, they may compress the root or cord and result in symptoms such as pain or weakness. Besides the increase in cyst size, pressure changes in extradural space as well as in arachnoid cyst might cause spinal cord compression and result in such symptoms2,6).
Pathogenesis and classification
The etiology of SEACs remains still unclear and can be congenital or acquired. SEACs are assumed to be the result of dural defects. Communication between the cysts and the intradural subarachnoid space has been reported in nearly all cases of arachnoid cysts6,8).
The cause of dural defect can be congenital or acquired. Trauma, arachnoiditis or iatrogenic cause can result in small dural tear and subsequent CSF accumulation to develop SEACs. Some reports demonstrated an association with dural ectasia or Marfan syndrome6). In this condition, a primary defect in the organization of collagen with decreased tensile strength weakens the ligamentous structures and other supporting tissues. Dural stretching can lead to dural thinning to such an extent that it becomes ectatic and even deficient in areas12). Although there is still debate in determining the etiology of SEACs, the theory of congenital dural defect is widely accepted12).
Dural defect is often found around the nerve root sleeves. One possible explanation is that tension across the movable dural sac and relatively fixed roots can predispose such dural tears. If patients have underlying structural abnormality such as Marfan syndrome, the probability of such tears may be further increased.
In our experience, both patients had no history of trauma, arachnoiditis or previous spine operation. No specific underlying disease was documented. Most authors believe that the cyst can be enlarged by pulsatile CSF dynamics and this theory can explain symptom fluctuation with exercise or valsava maneuver related to CSF dynamics5,6,13). There is limitation of understanding the pathogenesis of cyst development with osmotic gradient because there is lacking evidence of any difference of cystic fluid compared to CSF4). If in case of no communication, authors explained that the cyst developed by pulsatile CSF dynamics via a dural defect and the communication had been gradually closed over time and then disappeared4). On histopathologic examination, SEACs had no secretary function and the pathogenesis of active secretion by the cysts is invalid for explaining enlargement of the cysts.
Nabors et al.9) categorized SEACs in three major groups of meningeal cyst, non-meningeal epidural cysts, and neurenteric cysts. Meningeal cysts are further classified in 3 subgroups : 1) type 1 : extradural meningeal cyst that contains no neural tissue, 2) type 2 : extradural meningeal cyst that contains neural tissue, 3) type 3 : intradural meningeal cyst. Type 1 meningeal cysts consist of extradural arachnoid cysts (type Ia) and sacral meningoceles (type Ib).
The second case in current study is similar to the type 2 meningeal cyst categorized by Nabors et al. However, we propose a different lesson from the case when assuming the pathogenesis of cyst development. An trapped rootlet was found around the dural defect and we assumed it might contribute to cyst development. CSF leaks out via the dural defect and the rootlet caught in the defect interrupts its return into the subarachnoid space. This valve-like mechanism was previously described in several studies and the second case in this study can be another evidence supporting this mechanism7). The initial formation of the dural defect is assumed to be idiopathic.
Clinical outcome and surgical treatment
Signs and symptoms of SEACs are due to chronic cyst expansion and compression of the neural structures and thus, SEACs need surgical treatment. Diverse surgical techniques have been introduced and complete microsurgical resection of SEACs with merticulous repair of dural defect has been advocated as treatment of choice for SEACs13).
Alternatively, one report describes a selective interlaminar fenestration at the transdural communication site seen as pulsating flow voiding on preoperative cine-MRI at T12-L1 in a cyst from T1- to L3, with clipping of the dural rent and this resulted in subsequent cyst regression and improvement in clinical outcome. This technique has an apparent advantage of limited laminotomy but depends on precise preoperative planning of clip position at the communication site13).
Lee et al.6) demonstrated that the recurrence of the SEAC was related to the repair of the dural defect and not to the completeness of SEAC excision. To minimizaing the extent of laminectomy is important to avoid posteoperative complications such as kyphosis.
With improved diagnostic tools, we can verify the location of communication or dural defect preoperatively and it can help planning tailored laminotomy to avoid multi-level laminectomy and subsequent increased risk of complications. Currently many surgeons favor the tailored laminotomy and cyst fenestration with merticulous dural repair rather complete resection of SEACs to reduce the complication related to long-level laminectomy6,11,13).
We performed tailored laminectomy for cyst fenestration and repair of the dural defect and had good clinical and radiologic outcome.
CONCLUSION
We have experienced two cases of SEACs and performed tailored laminectomy and cyst fenestration with dural repair in these cases. Clinical and radiologic outcome was excellent in both cases and there has not been any evidence of cyst recurrence till now.
In the second case, a loop of single rootlet was found got stuck within the dural defect and it might contribute to develop the cyst by inhibiting spontaneous dural closure. It is a rare case and can be considered as another etiology of SEACs.